DNS
DNS is one of the most important services for internet because is necessary to convert a name of one web in its IP for simply question: Remember a IP is very most difficult that remember a name.
At first for to do it the first computers had a simply file called host.txt that works similar to key/value dictionary: One name have one IP translation. And one of this old computers is used to serve the HOSTS.txt updated of the rest of old computers. This is the concept.
This is simply if you have less than 10 computers in the world. But now, this is a bit complicated with too much computers.
The DNS service is regulated by the ICANN since 1988.
Basically for understand how ICANN regulated it you must know that she designates a root nodes to keep all information about how to resolve whatever domain. When you go to website to register a website name, actually you are recording your domain in the ICANN nodes.
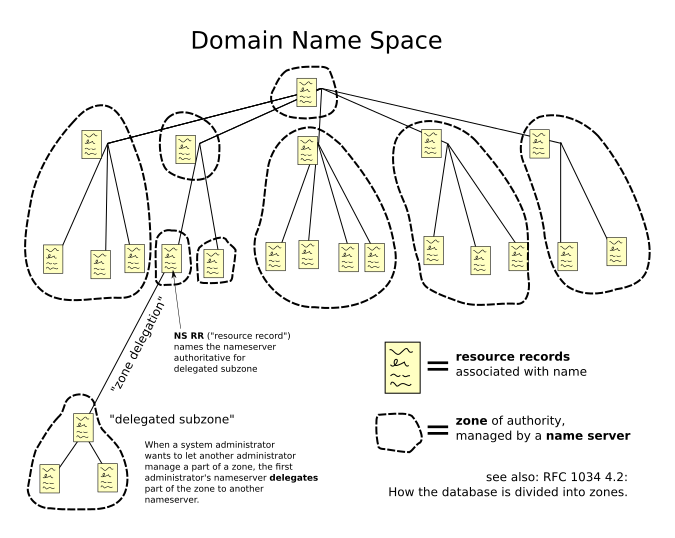
Each domain have different records for the dommain. A record is the basic data component in DNS. Resource records define not only names and IP addresses but domains, servers, zone, and services as well. This list shows you the most common types of resource records:
| Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| A | Address resource records match an IP address to a host name. |
| CNAME | Canonical name resource records associate a nickname to a host name. |
| MX | Mail exchange resource records identify mail servers for the specified domain. |
| NS | Name server resource records identify servers (other than the SOA server) that contain zone information files. |
| PTR | Pointer resource records match a host name to a given IP address. This is the opposite of an Address record, which matches an IP address to the supplied host name. |
| SOA | Start of authority resource records specify which server contains the zone file for a domain. |
| SRV | Service resource records identify servers that provide special services to the domain. |
DNS Query
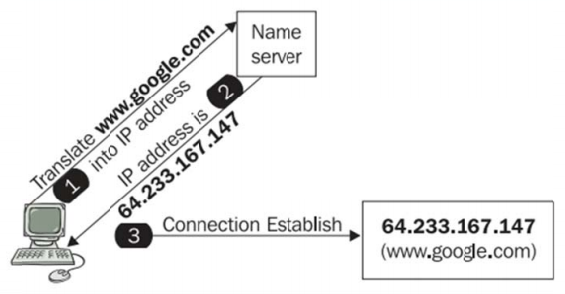
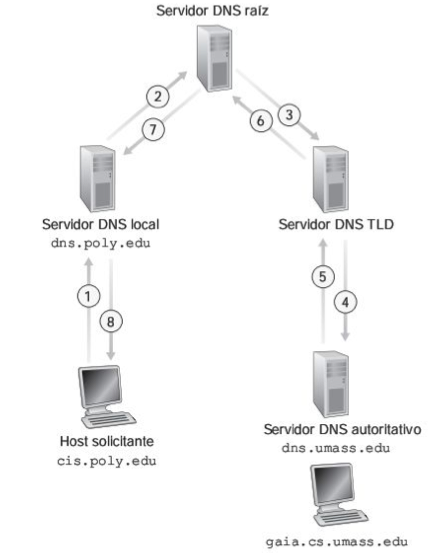
The better way to explain the process is with a example.
You need to know the resolve of www.google.com domain.
Iterative Query
- Client query here local DNS. (1)
- If the local DNS don't know the domain, answer the root nameserver. (2)
- Root Nameserves indicate the node that have
.com>googleregister. - Local DNS talk with the node and obtain the DNS authority nameserver. (4)(5)
- Local DNS contact with DNS authority nameserver for resolve
www - DNS authority nameserver respond local DNS.
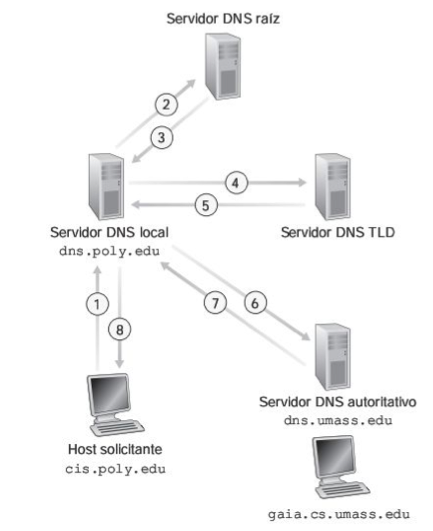
This is normally to process to resolve a query.
Recursive Query
The process with recusive query is similar, but now the DNS local doesn't handle all calls: The DNS servers delegate in others DNS server to resolve the query.
DNS Respond
The server that respond the query is indicate in the AA (Authoritative Answer). Its possible that for each zone have more than one DNS name server. This is known as Primary and Secondary DNS of the zone and data redundancy is a measure of safety and reliability.
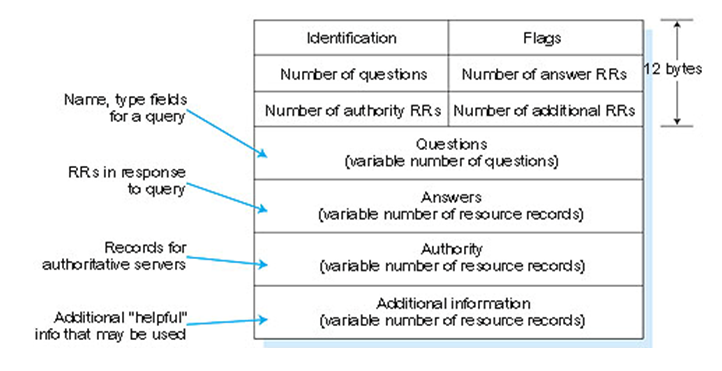
In easy see this in the DNS response message: